 (
( (
( (
( (
(| Quantity in the Full-Size Model | Quantity in the Scaled Model | Relationships | ||||
| Coordinates | x |  | x = S |
|||
| y |  | y = S | ||||
| z | z = Sz | |||||
| Frequency | f | f = | ||||
| Complex relative | 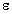 ' ' |
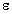 ' = ' = |
||||
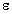 " " |
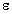 " = " = |
|||||
| Conductivity | 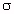 | 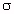 = = | ||||
| SAR | SAR |  | SAR =  /S /S |
 /f = 100 MHz/13.56 MHz = 7.38.
/f = 100 MHz/13.56 MHz = 7.38.
| Full-Size Model | Scaled Model | |||
| Sphere diameter | d = 52 cm | d = d/S = 52/7.38 = 7.05 cm | ||
| Frequency | f = 13.56 MHz |  = Sf = 7.38 x 13.56 = 100 MHz = Sf = 7.38 x 13.56 = 100 MHz | ||
| Permittivity | 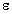 ' = 149 ' = 149 |  = =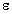 ' = 149 ' = 149 | ||
| Conductivity | 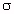 = 0.62 S/m = 0.62 S/m |  = S = S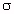 = 7.38 x 0.62 = 4.58 S/m = 7.38 x 0.62 = 4.58 S/m | ||
| SAR | (Calculated) SAR = 0.54 W/kg | (Measured) |